Different types of injection molding processes
The injection molding technique has revolutionized numerous industries, enabling efficient production of high-quality products and services for the global market. From automotive to consumer electronics, injection molding processes have played a pivotal role in shaping the world we live in. But have you ever wondered when and how injection molding is used? Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the diverse applications and innovative methods behind molding a wide range of materials. Get ready to dive into the exciting realm of injection molding and unlock the secrets of its versatility!
How does injection molding work?
Injection molding is creating parts by injecting molten material into a mold. The process is common for plastics but also works for metals, glass, and ceramics. The first step is the creation of the mold of the desired product. And then place put the mold on the injection molding machine.
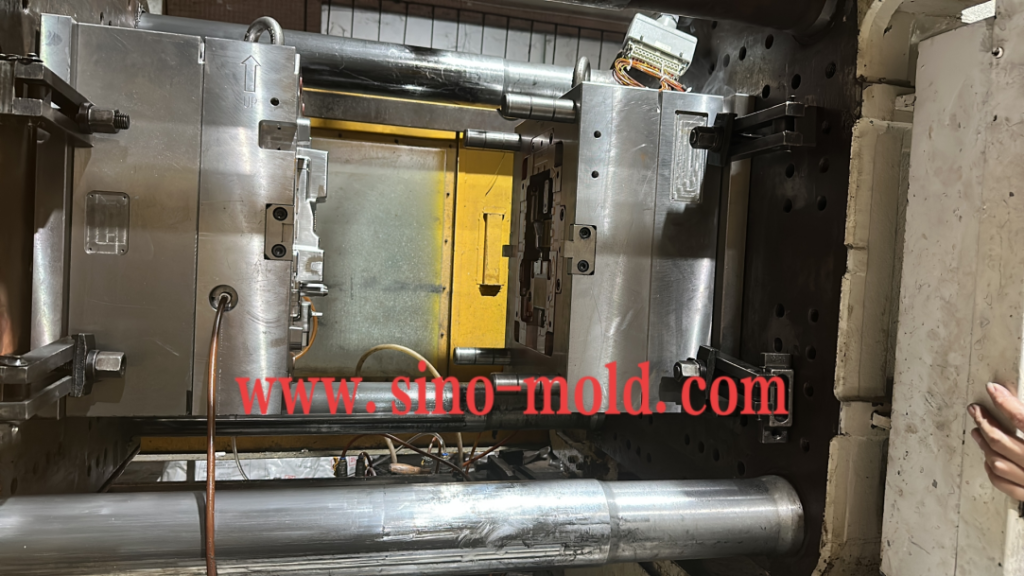

The second step is to heat the plastic resin like the one shown below until they are melted.

The molten plastic resin then goes into the mold under high pressure. When the material cools and hardens, it takes on the shape of the mold cavity. Finally, the part or product ejects from the mold.
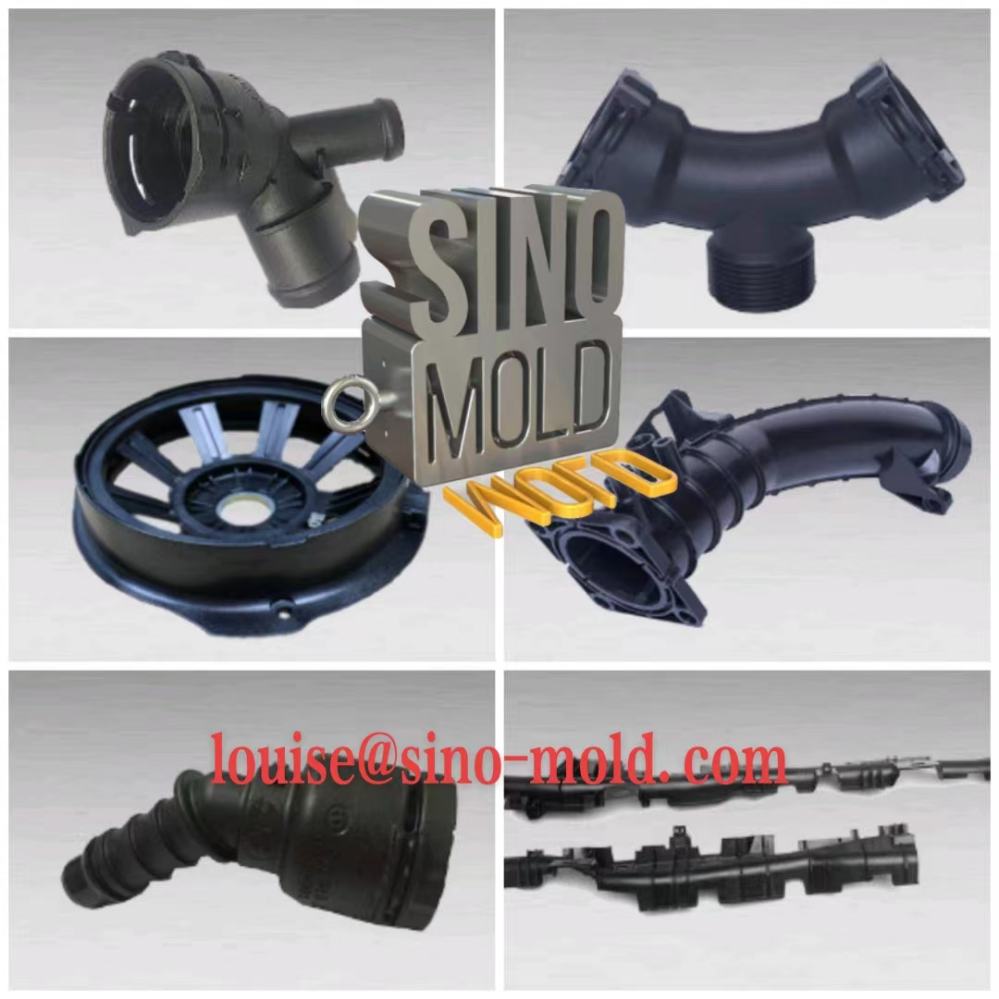

Using different types of injection molding processes, you can create parts of all shapes and sizes including standard plastic items like bottle tops and remote control casings, syringes, and more. It is also commonly used for manufacturing more oversized items such as car body panels. This article will introduce some different types of injection molding processes.
#injectionmold #moldsupperlier
Die casting

Die casting starts with the creation of a mold, typically made of steel, consisting of two halves: the fixed die and the ejector die. The mold is designed to form the desired shape of the part. The molten metal, usually aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, is injected into the mold cavity using a high-pressure casting machine. Once the metal solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Types of Die Casting:
Hot Chamber Die Casting: This method is used for metals with low melting points, such as zinc and magnesium.
Cold Chamber Die Casting: Cold chamber die casting is suitable for metals with high melting points, such as aluminum.
Advantages :
High precision and dimensional accuracy
Excellent surface finish
High production rates
Cost-effective
Metal injection molding

Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a versatile manufacturing process that combines the benefits of plastic injection molding with the strength and durability of metals.
Several key steps of The Metal Injection Molding
Feedstock Preparation: Fine metal powders are mixed with a binder material to create a homogeneous feedstock.
Injection Molding: The feedstock is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure using an injection molding machine.
Debinding: The molded parts, undergo a debonding process where the binder is removed.
Sintering: The rebound parts are then subjected to a high-temperature sintering process, where they are heated to near the melting point of the metal. This results in the removal of the remaining binder material and the fusion of metal particles, leading to the densification of the parts.
Finishing Operations: such as machining, and polishing.
advantages:
Complex Geometries can be done;
High Precision;
Material Versatility;
Cost Efficiency;
Scalability;
Over molding

Overmolding is a specialized injection molding process that involves the application of a second layer of material onto an existing substrate or component. This technique allows for the combination of different materials, offering enhanced functionality, improved ergonomics, and aesthetic appeal in product design
Over-molding steps:
Substrate Preparation: The initial component or substrate is prepared by molding or fabricating it separately.
Injection Molding: The pre-mold is placed into the mold cavity of the injection molding machine, and a second material is injected over it.
Bonding and Solidification: The over-mold material bonds with the pre-molded substrate as it cools and solidifies, creating a single integrated part.
Finishing Operations: such as trimming, machining, or surface treatment.
Advantages
Enhanced Functionality;
Improved Aesthetics;
Increased Durability and Protection.
Cost Efficiency;
Design Flexibility;
Insert molding

Insert molding is a specialized injection molding process that combines metal or plastic inserts with molten thermoplastic material to create a single integrated component. This technique offers numerous advantages, including increased strength, improved functionality, and simplified assembly.
Insert Molding steps:
Insert Placement: The metal or plastic inserts, such as threaded fasteners, electronic components, or other pre-fabricated parts, are placed into the mold cavity.
Injection Molding: The molten thermoplastic material is injected into the mold cavity.
Cooling and Solidification
Ejection and Finishing: The mold is opened, and the finished part, including the molded-in inserts, is ejected. Additional post-processing, such as trimming or surface treatment.
Advantages
Enhanced Strength: The integration of inserts improves the structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities of the component.
Reduced Assembly Steps
Improved Functionality: such as electrical conductivity, heat dissipation, or threaded connections.
Design Flexibility: Insert molding enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs by combining different materials and incorporating diverse inserts.
Cost Efficiency: insert molding offers long-term cost savings through streamlined production, reduced material waste, and improved product performance.
Thin-wall injection molding

Thin wall injection molding is a specialized manufacturing process that allows for the production of thin-walled plastic parts with minimal wall thickness. This technique offers numerous advantages, including lightweight design, cost efficiency, and high-speed production.
Thin-Wall Injection Molding steps:
Material Selection: High-flow thermoplastic materials, such as PP or PS, are commonly used for thin-wall molding due to their excellent flow properties.
Injection Molding: The molten plastic material is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure and high speed to ensure quick and even filling of the thin walls.
Cooling and Ejection
Advantages
Lightweight Design: The reduced wall thickness of thin-wall parts results in lighter components, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
Cost Efficiency.
Enhanced Functionality: such as intricate designs, snap-fit connections, or integrated cooling channels.
Design Freedom.
Environmental Sustainability.
Liquid silicone injection molding.

Liquid silicone injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process that allows for the production of high-quality silicone components with exceptional precision, durability, and versatility. This technique utilizes liquid silicone rubber (LSR) material, which is injected into a mold cavity under controlled conditions, creating complex, durable, and dimensionally accurate parts.
Liquid Silicone Injection Molding steps:
Material Preparation: Liquid silicone rubber (LSR)
Injection Molding: The LSR material is injected into the mold cavity using a precision injection molding machine
Curing and Solidification: The injected LSR material is cured or vulcanized within the mold cavity, transforming it from a liquid to a solid elastomer.
Mold Opening and Ejection.
Advantages
Design Flexibility: The liquid nature of LSR allows for the replication of intricate details, thin walls, and complex geometries with high precision.
Material Properties: LSR exhibits excellent properties, including high thermal stability, chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and electrical insulation properties.
Consistency and Reproducibility.
Overmolding Capability: LSR can be over-molded onto other substrates or components,
Reduced Waste and Assembly.
Reaction injection molding
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM) is an advanced manufacturing process that combines liquid components to create high-quality polyurethane (PU) parts. Unlike traditional injection molding, RIM utilizes a chemical reaction between two or more liquid reactants to form a solid component. This technique offers numerous advantages, including design flexibility, lightweight construction, and the ability to produce complex, durable parts.

Reaction Injection Molding Steps:
Material Preparation: Two or more liquid components are mixed together in precise ratios and under controlled conditions.
Injection and Mixing: The mixed liquid reactants are injected into a closed mold cavity using a high-pressure mixing head.
Chemical Reaction and Solidification: The injected reactants undergo a chemical reaction.
Mold Opening and Part Removal.
Advantages:
Design Freedom;
Durable and Lightweight Parts;
The Versatility of Material Properties
Reduced Cycle Time;
Improved Part Consolidation.
Micro injection molding
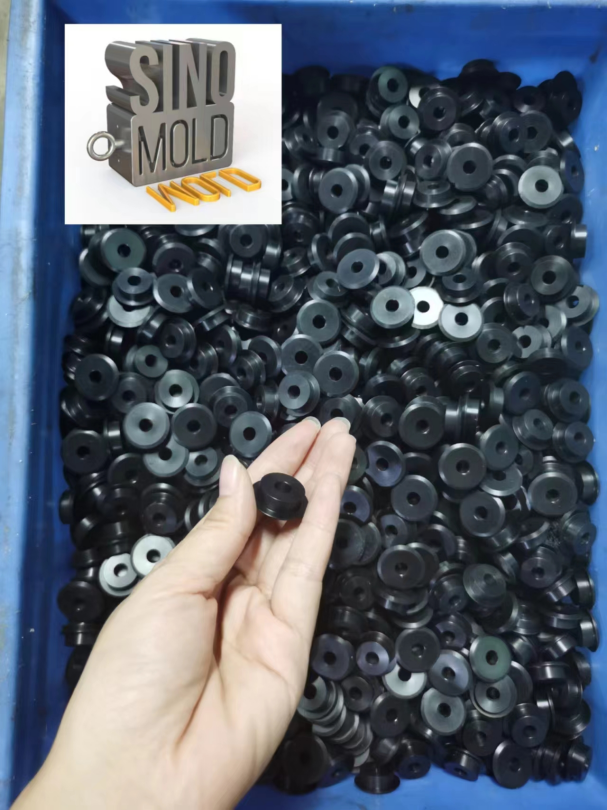

Micro injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process that allows for the production of miniature components with high precision and intricate details. This technique utilizes specialized equipment and molds to inject thermoplastic materials into micro-sized cavities, resulting in the creation of small, complex parts.
Micro injection molding steps:
Material Selection: Thermoplastic materials with excellent flow properties.
Injection Molding: The molten thermoplastic material is injected into the micro-sized mold cavity with high precision and control.
Cooling and Solidification.
Advantages
High Precision
Miniature Size Capability
Material Selection
Cost Efficiency
Enhanced Functionality
Gas-assisted injection molding
Gas-assisted injection molding is an innovative manufacturing technique that enhances the design, functionality, and performance of plastic components by incorporating internal gas channels. This process involves the injection of molten plastic into a mold cavity, followed by pressurized gas to displace the material and create hollow sections or intricate internal features.
Gas-Assisted Injection Molding steps:
Material Injection: Molten plastic material is injected into the mold cavity, partially filling the space while leaving room for the internal gas channels.
Gas Injection: Once the material solidifies around the gas channels, pressurized gas, typically nitrogen, is introduced into the channels, displacing the molten plastic and forming hollow sections or creating internal features.
Cooling and Solidification.
Advantages
Hollow Sections and Lightweight Design
Improved Aesthetic Appearance
Enhanced Design Flexibility.
Reduced Residual Stresses
Thermoplastic Injection Molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that enables the production of high-quality plastic components with excellent precision, consistency, and cost efficiency. This technique involves injecting molten thermoplastic material into a specially designed mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify, resulting in the formation of the desired part.

Thermoplastic Injection Molding steps:
Material Preparation: Thermoplastic resins, selected based on desired properties and application requirements, are prepared by melting them into a molten state.
Injection: The molten thermoplastic material is injected under high pressure into the mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system.
Cooling and Solidification
Mold Opening and Ejection
Conclusion:
Injection molding offers various processes to cater to different manufacturing needs. From conventional molding for standard parts to two-shot molding for multi-material components, each process provides distinct advantages. Whether it’s achieving complex designs, improving part strength, or reducing assembly steps, injection molding continues to evolve and revolutionize the manufacturing industry with its versatility and efficiency. Understanding the various types of injection molding processes empowers manufacturers to choose the most suitable approach for their specific application requirements.
If you have any additional questions about what injection molding technology your part may need, we’d love to help out. Welcome to Sino-Mold Industrial.,Ltd
