Introduction to Unscrewing Plastic Injection Molds:
Unscrewing molds are a specialized type of plastic injection mold used in the manufacturing industry. They are designed to produce intricate plastic parts with internal threads or undercuts that cannot be ejected from a traditional plastic injection mold all in a single piece.
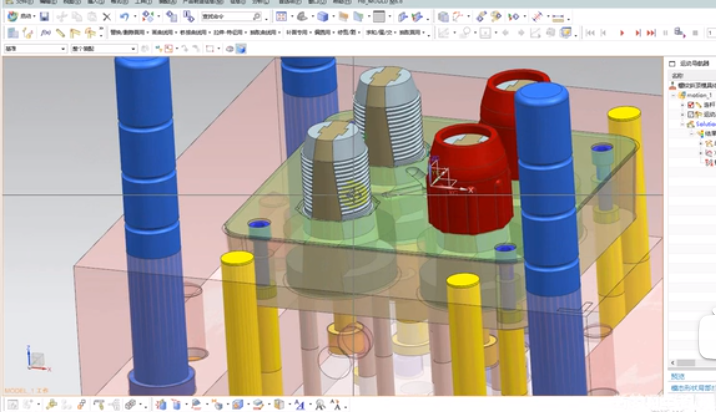
Definition and Purpose:
Unscrewing molds are aptly named for their ability to unscrew or rotate cores within the mold cavity to release complex parts. This rotational movement allows for the removal of parts with threads or other features that would otherwise become trapped during ejection.
How do Unscrewing Molds Work?
Mechanism and Functionality:
Unscrewing molds are essential tools in injection molding for producing intricate plastic parts with internal threads or undercuts. These molds typically consist of two halves: a stationary mold half and a movable mold half. The unscrewing mechanism is integrated into the movable mold half and is responsible for rotating the core components to facilitate the release of molded parts. This operation exemplifies a unique plastic injection molding process, highlighting its distinctiveness in manufacturing components with detailed threads. A hydraulic cylinder is commonly used to drive the rotational movement of the core components, providing the force necessary for the gear train of force transmission.
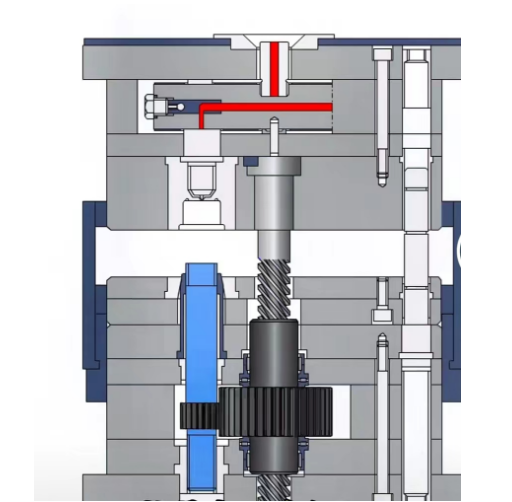
Mold technology, particularly in the context of unscrewing molds, plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity of the threaded components produced. It emphasizes the importance of the unique injection molding process and the careful handling required to maintain the quality of the intricate threading patterns.
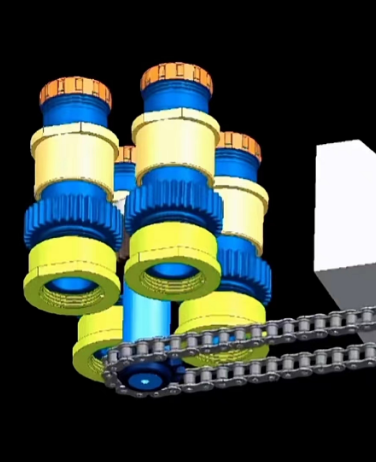
Components of Unscrewing Molds:
Stationary Mold Half: This half of the mold remains fixed in position during the molding process and provides the foundation for the mold cavity and core.
Movable Mold Half: The movable mold half houses the unscrewing mechanism and is designed to open and close to allow for part ejection.
Unscrewing Mechanism: The unscrewing mechanism is the heart of the unscrewing mold system. It typically comprises hydraulic or electric actuators that drive the rotational movement of the core components. The core is responsible for forming the internal features of the molded part, such as threads or undercuts.
Understanding the Core Principles:
The unscrewing mold process requires precise coordination between the mold design, molding machine, and unscrewing mechanism to ensure smooth operation and high-quality parts. The production of detailed threads in components like bottle caps and nuts emphasizes the need for precision in the unscrewing molds to maintain the strength, tolerance, and smoothness of these threads without causing damage.
Mold Design: The design of the unscrewing mold must take into account the geometry of the part, including the location and orientation of internal features. Proper venting and gating are essential for mold technology to facilitate part ejection without causing defects.
Molding Machine: The molding machine provides the hydraulic or electric power necessary to actuate the unscrewing mechanism. The machine’s control system coordinates the movement of the mold halves and the unscrewing mechanism to ensure precise timing and alignment.
Unscrewing Mechanism Operation: As the mold opens during the ejection phase of the molding cycle, the unscrewing mechanism engages to rotate the core components. This rotational movement allows the molded part to disengage from the core and be ejected from the mold cavity.
Smooth Ejection: By rotating the core components, the unscrewing mechanism ensures that the molded part is released smoothly and without damage. Proper lubrication and maintenance of the unscrewing mechanism are essential to prevent binding or excessive wear.
Key Components of Unscrewing Molds
Exploring the Essential Parts:
Core and Cavity Inserts: These are the primary components responsible for forming the shape of the molded part, crucial in precision multi-cavity plastic injection molds for producing threaded plastic parts such as bottle caps, shampoo bottles, pharmaceutical supplies, automotive parts, and more. The core and cavity inserts are typically precision-machined to ensure the accurate replication of part geometry, emphasizing the need for high-quality, reliable unscrewing plastic injection molds that operate at high speeds to reduce cycle times and part costs, particularly for high-volume applications.
Unscrewing Mechanism: The unscrewing mechanism is the heart of unscrewing molds, enabling the rotational movement of cores to release parts with internal threads or undercuts. Common unscrewing mechanisms include hydraulic cylinders and electric motors, which provide the necessary driving force for core rotation. This is particularly vital in plastic injection molding for high-speed, high-volume production across various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and cosmetics packaging.
Guiding Systems: Guiding systems are integral to maintaining precise alignment and smooth operation during the unscrewing process. They ensure that the moving components, such as cores, align correctly with the stationary components to prevent binding or misalignment.
Cooling Channels: Efficient cooling is essential for achieving high-quality molded parts and minimizing cycle times. Cooling channels integrated into the mold base help dissipate heat from the molten plastic, maintaining consistent temperature control throughout the molding process.
Mold Base: The mold base provides the structural support and mounting platform for all other components of the mold. It serves as the foundation upon which the core and cavity inserts, guiding systems, and cooling channels are assembled.
Components and Their Functions:
Core and Cavity Inserts: These precision-machined components define the shape and features of the molded part, including any internal threads or undercuts.
Unscrewing Mechanisms: Hydraulic cylinders or electric motors drive the rotational movement of cores, allowing for the release of parts with intricate internal features.
Guiding Systems: These systems ensure precise alignment of moving components during the unscrewing process, minimizing the risk of misalignment or binding.
Cooling Channels: Integrated into the mold base, cooling channels help regulate the temperature of the mold, promoting consistent cooling of the plastic material and enhancing part quality.
Applications of Unscrewing Molds for Threaded Plastic Parts
Industries and Products Utilizing Unscrewing Molds:
Automotive: Unscrewing molds find extensive use in the automotive industry for manufacturing components such as gearshift knobs and fuel caps. These parts, including threaded components, often feature intricate internal threads or undercuts, which can be efficiently produced using unscrewing molds. The technology is crucial for creating durable and precise threaded plastic parts in vehicles, from small interior elements to critical engine components.

Medical: In the medical sector, unscrewing molds are employed for producing critical components like syringe parts and IV connectors. The precision and reliability of unscrewing molds are essential for meeting stringent quality standards in medical device manufacturing, ensuring the production of threaded components that are vital for the functionality and safety of medical devices.

Consumer Goods: Unscrewing molds play a vital role in the production of consumer goods such as cosmetic containers and electronic housings. These molds enable the creation of complex part geometries with internal features, including threaded plastic parts, meeting the demands of modern product designs. This technology is particularly important for producing a wide range of consumer products, from cosmetic packaging with intricate threading to household items requiring precise thread patterns for functionality. Unscrewing molds are specifically designed to produce threaded components, including intricate parts such as bottle caps and, closures, and automotive components, showcasing the versatility of unscrewing molds in various applications.

Versatility and Flexibility in Application:
Unscrewing molds offer unparalleled versatility and flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of industries and product designs. Unscrewing molding is particularly effective for producing parts with intricate internal threads or undercuts, thanks to its unique process involving movement and rotation. Their ability to produce parts with intricate internal threads or undercuts enhances design possibilities and enables the creation of complex components. Whether in automotive, medical, or consumer goods manufacturing, unscrewing molds demonstrate their adaptability and efficiency in meeting diverse production requirements.
Benefits of Unscrewing Molds
Advantages Over Traditional Molding Methods:
Ability to Mold Complex Parts: Unscrewing molds excel in producing parts with intricate internal threads and undercuts, which are challenging to manufacture using traditional molding methods. This capability expands design possibilities and allows for the creation of complex components.
Reduced Secondary Operations: Compared to traditional molding processes, unscrewing molds minimize the need for secondary machining operations and assembly steps. This reduction in post-processing tasks not only saves time but also lowers production costs and improves overall efficiency. Electric driven unscrewing mold designs facilitate clean and easy setup for each production molding, enhancing the efficiency and reducing cycle times for high-volume production.
Improved Part Quality: Unscrewing molds contribute to enhanced part quality and consistency by ensuring precise molding of intricate features. The controlled rotational movement of the cores results in uniform part geometry and minimizes the risk of defects, leading to superior finished products.
Enhanced Precision and Efficiency:
Unscrewing molds offer superior precision and repeatability, leading to higher quality molded parts with tight tolerances. The elimination of secondary machining operations streamlines the manufacturing process, reducing lead times and enhancing overall efficiency. By optimizing production workflows and minimizing manual interventions, unscrewing molds enable manufacturers to achieve greater productivity and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Design Considerations for Unscrewing Molds
Factors Influencing Design Choices:
Part Geometry and Complexity: The design of unscrewing molds is heavily influenced by the geometry and complexity of the molded parts. Complex features, such as internal threads and undercuts, require careful consideration to ensure proper mold functionality and part ejection.
Material Selection: The choice of material for both the mold components and the molded parts plays a crucial role in unscrewing mold design. High-quality materials are essential for unscrewing plastic injection molds, especially in high-volume applications like bottle caps, shampoo bottles, and automotive parts, to reduce cycle times and part costs. Factors such as material properties, shrinkage rates, and thermal conductivity must be carefully evaluated to achieve the desired part quality and dimensional accuracy, while also ensuring the mold operates at high speed and complexity to prevent damage to threaded plastic parts during the removal process.
Tolerance Requirements: Tight tolerance requirements necessitate precise mold design and manufacturing processes. The mold design must account for dimensional variations and ensure consistent part quality throughout the production run.
Production Volume: The anticipated production volume influences design decisions regarding mold complexity, tooling costs, and maintenance requirements. High-volume production may require more durable mold materials and automated unscrewing mechanisms to ensure long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Importance of Precision Engineering:
Successful unscrewing mold design relies on meticulous attention to detail and precision engineering. Close collaboration between mold designers, toolmakers, and injection molders is essential to ensure optimal mold performance and part quality. Iterative design refinement and rigorous testing help identify potential issues early in the process, allowing for adjustments to be made before full-scale production. By prioritizing precision engineering principles, manufacturers can achieve reliable and efficient unscrewing mold solutions that meet the stringent requirements of modern manufacturing environments.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Issues Faced with Unscrewing Molds:
Thread Distortion: The unscrewing process can sometimes cause distortion or damage to the threads of molded parts, leading to compromised functionality or assembly issues.
Core Binding: Inefficient or improper core movement can result in core binding, where the core becomes stuck or difficult to rotate, affecting part ejection and mold performance.
Wear and Tear on Unscrewing Mechanisms: Continuous operation of unscrewing mechanisms can lead to wear and tear over time, affecting their reliability and longevity.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges:
Implementing Proper Mold Maintenance Procedures: Regular maintenance and inspection of unscrewing molds are essential to prevent issues such as thread distortion and core binding. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and periodic replacement of worn components.
Optimizing Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Proper cooling and lubrication systems help minimize friction and heat buildup during the unscrewing process, reducing the risk of thread distortion and core binding. Cooling channels should be strategically designed to ensure uniform temperature distribution and efficient heat dissipation.
Conducting Thorough Testing and Validation: Comprehensive testing and validation procedures are crucial to identify and address potential issues with unscrewing molds before full-scale production. This may involve prototyping, mold trials, and performance testing to ensure smooth core movement, minimal wear on unscrewing mechanisms, and consistent part quality. Regular monitoring and adjustments based on performance feedback further optimize mold functionality and longevity.
Conclusion
Recap of Unscrewing Mold Significance:
Unscrewing molds plays a crucial role in the production of complex plastic parts with internal and external threads, and undercuts. Their versatility, precision, and efficiency make them indispensable in various industries, from automotive to medical devices.
Final Reflections on their Importance:
As manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, unscrewing molds remain at the forefront of innovation, enabling the production of increasingly intricate and functional plastic components.
Call to Action
Do you have questions about unscrewing molds or need assistance with your next project? Our team of experts at Sino-Mold Industrial Co., Ltd. is here to help. Reach out to us at www.sino-mold.com or email us at sales02@sino-mold.com for personalized guidance and support tailored to your specific needs. Let’s bring your vision to life with precision and efficiency.
